



When electrons slowly vanish during cooling
Baku, August 3, AZERTAC
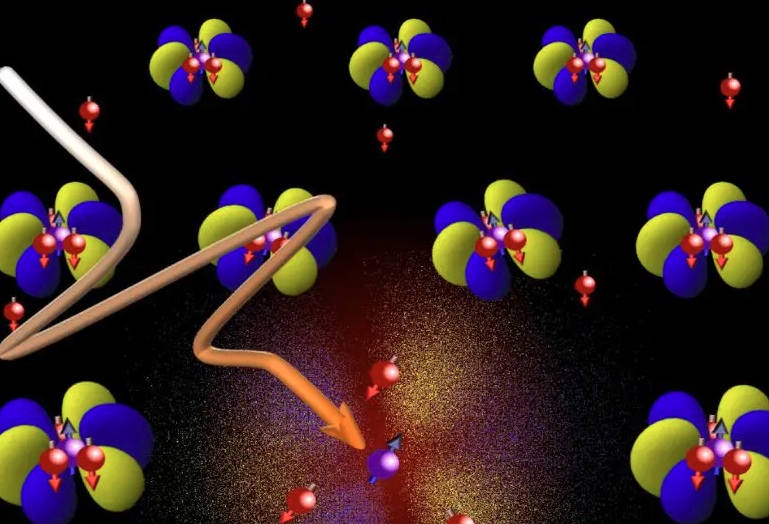
Many substances change their properties when they are cooled below a certain critical temperature. Such a phase transition occurs, for example, when water freezes. However, in certain metals there are phase transitions that do not exist in the macrocosm. They arise because of the special laws of quantum mechanics that apply in the realm of nature's smallest building blocks. It is thought that the concept of electrons as carriers of quantized electric charge no longer applies near these exotic phase transitions. Researchers have now found a way to prove this directly. Their findings allow new insights into the exotic world of quantum physics. Many substances change their properties when they are cooled below a certain critical temperature. Such a phase transition occurs, for example, when water freezes. However, in certain metals there are phase transitions that do not exist in the macrocosm. They arise because of the special laws of quantum mechanics that apply in the realm of nature's smallest building blocks. It is thought that the concept of electrons as carriers of quantized electric charge no longer applies near these exotic phase transitions. Researchers at the University of Bonn and ETH Zurich have now found a way to prove this directly. Their findings allow new insights into the exotic world of quantum physics. The publication has now been released in the journal Nature Physics.
If you cool water below zero degrees Celsius, it solidifies into ice. In the process, it abruptly changes its properties. As ice, for example, it has a much lower density than in a liquid state -- which is why icebergs float. In physics, this is referred to as a phase transition.
But there are also phase transitions in which characteristic features of a substance change gradually. If, for example, an iron magnet is heated up to 760 degrees Celsius, it loses its attraction to other pieces of metal -- it is then no longer ferromagnetic, but paramagnetic. However, this does not happen abruptly, but continuously: The iron atoms behave like tiny magnets. At low temperatures, they are oriented parallel to each other. When heated, they fluctuate more and more around this rest position until they are completely randomly aligned, and the material loses its magnetism completely. So while the metal is being heated, it can be both somewhat ferromagnetic and somewhat paramagnetic.
Azerbaijan, Association of International Educators discuss opportunities for cooperation
Türkiye's Bayraktar TB3 UAV breaks altitude record
Baku Higher Oil School, Tashkent Institute of Chemical Technology explore cooperation opportunities
Stele from Nomgon-2 complex presented
Student from Baku Higher Oil School achieves top result in master’s program exams